Microcontrollers and boards
Reminder - Computer architecture
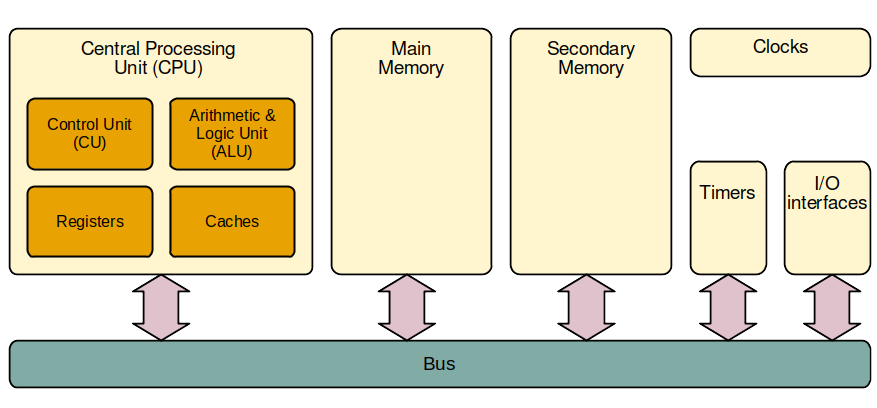
- Main memory: RAM (see further)
- Secondary memory:
- hard drive
- SSD (Flash)
- I/O interfaces: for keyboard(s), mouse/mice, monitor(s), printer(s), network(s), etc.
- When multiple CPUs: more complicated
RAM: Random Access Memory
SSD: Solid State Drive
SSD: Solid State Drive
Example - IBM z16 A01
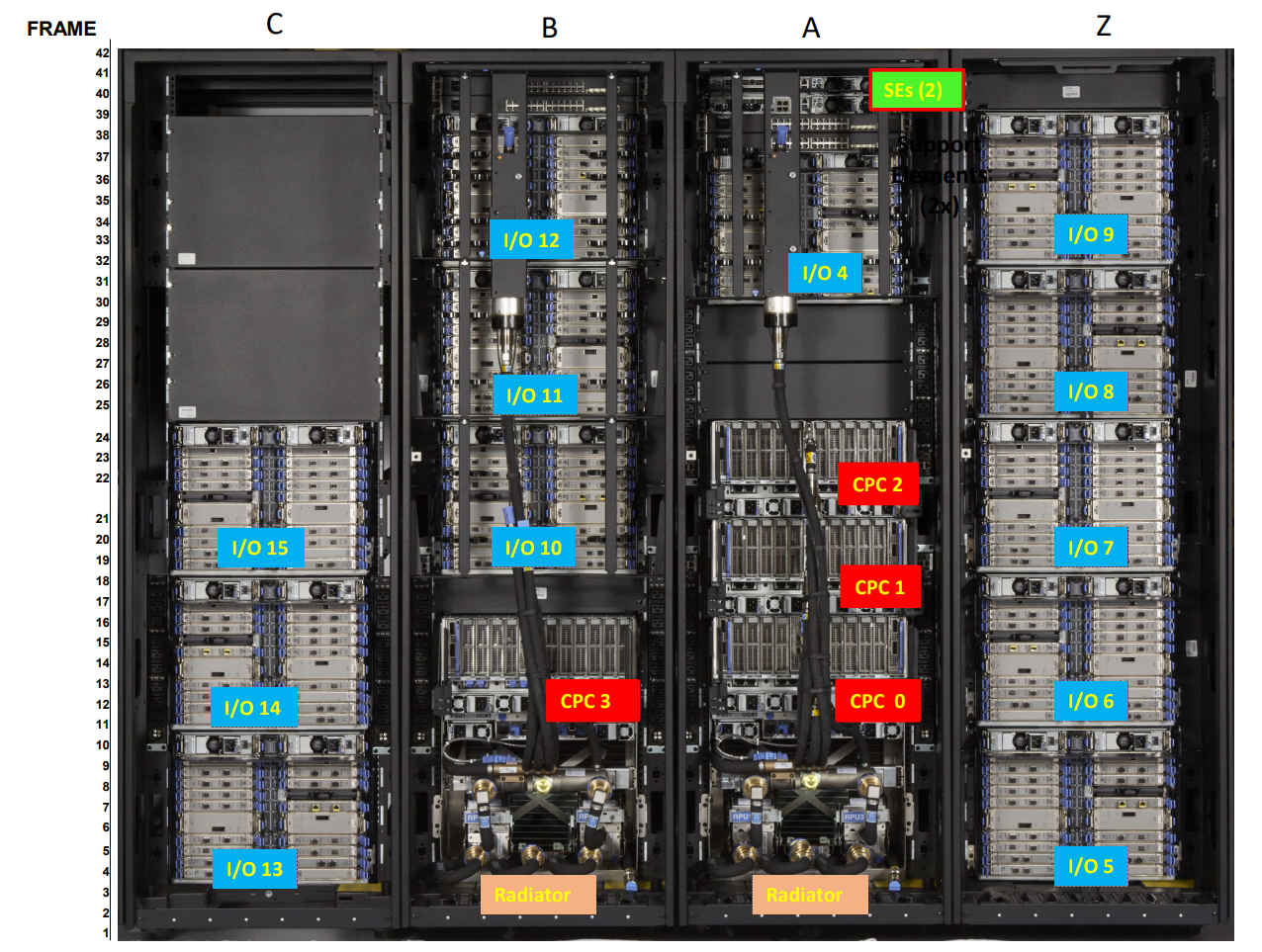
- 4 cabinets, each measuring approximately 48 x 185 cm
- Maximum memory: 40 TB
CPC: Central Processor Complex
Source:
IBM
Example - Desktop PC

Source: PB
Example - BeagleBone Black SBC
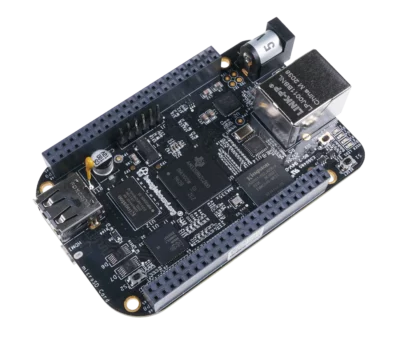
SBC: Single Board Computer
Source:
beagleboard.org
- The BeagleBone Black can be used as a general purpose computer
- It can also be used as an embedded system
- ⇒The definition in the previous section should not be taken strictly
Many different SBCs exist.
Continuing with integration
- What about an Integrated Circuit (IC) containing one (or more) CPU(s), some memory, and I/O interfaces?
- This is a microcontroller (MCU - MicroController Unit)
Microcontroller architecture
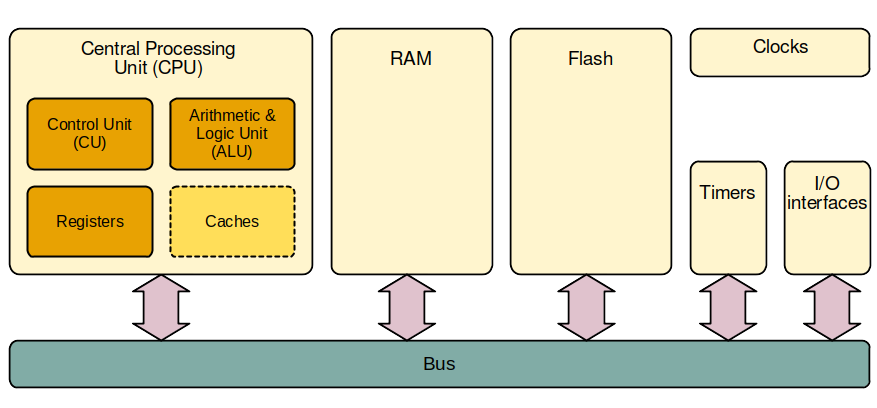
- Some microcontrollers may have one or more caches
- No more primary/secondary memory but RAM/Flash (see further) instead
Microprocessor vs microcontroller
- A microprocessor (MPU - MicroProcessor Unit) contains one (or more) CPU(s) and some I/O interfaces
- Most computers are based on microprocessors.
Reminder - Memory content retention
- RAM is volatile memory: content is lost when the system is turned off
- Flash is non-volatile memory
- You may find other acronyms: ROM, PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, FRAM, MRAM, etc.
RAM: Random Access Memory - ROM: Read-Only Memory - PROM: Programmable ROM
- EPROM: Erasable Programmable ROM - EEPROM: Electrically Erasable ROM
- FRAM: Ferroelectric RAM - Magnetoresistive RAM
Important: flash memory can only accept a limited number of writes.
- Depending on memory type: between 10,000 and 1 million writes
- Wear-leveling algorithms: spread out write operations
Microcontroller architecture - more details
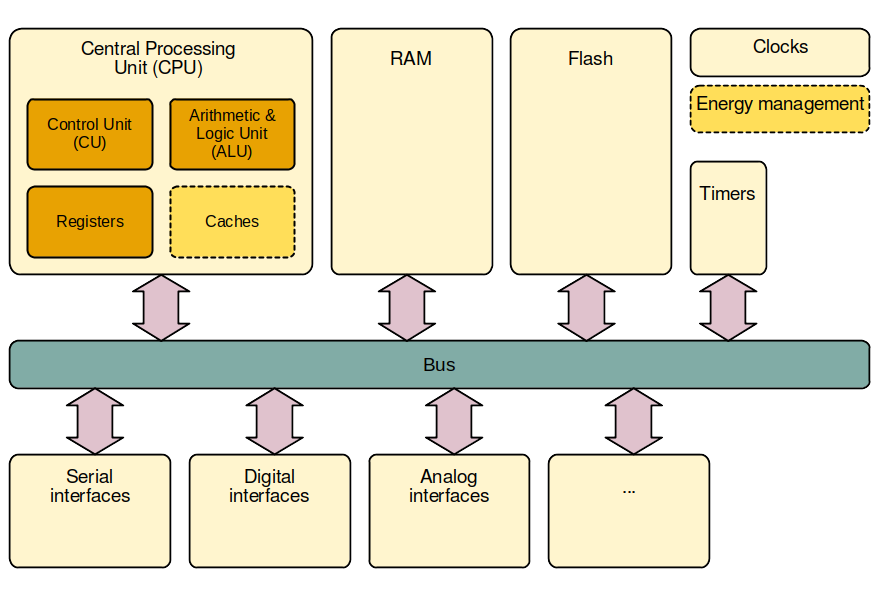
- I/O interfaces: different types (see further)
- Peripherals may be included (see further)
- Energy management: on low power consumption microcontrollers
Embedded system
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
- A microcontroller
- Additional elements (see next diagram)
- Case
The name device is also used.
Board architecture
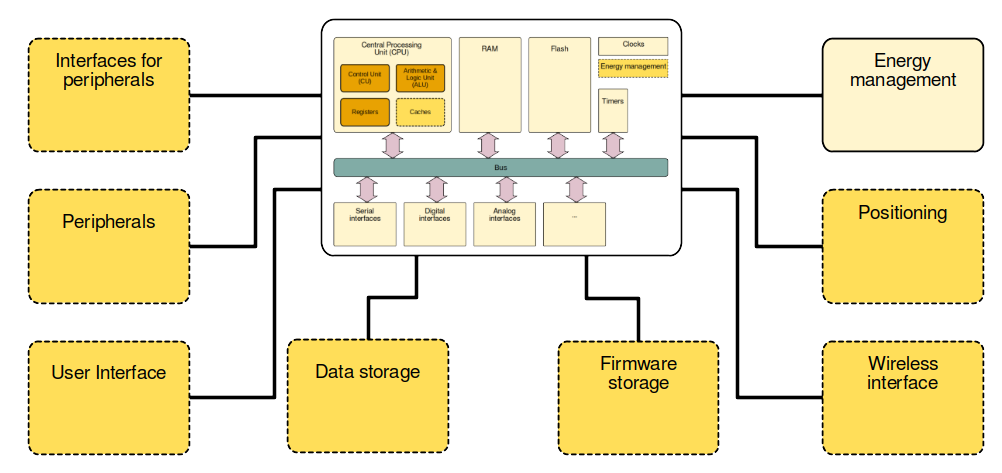

Energy management:
- Voltage regulator
- Protection against voltage inversion
- Battery management system
- Etc.
Wireless interface:
- May be provided by the MCU
Data storage:
- To store large amounts of data
Firmware storage:
- To implement Over-The-Air (OTA) update
Example - EFR32BG24 Dev Kit

Important board/microcontroller characteristics?
- Depend on the target application!
- Example of characteristics to consider:
- Extensions and/or libraries for ML support
- Serial interfaces
- Digital interfaces
- Analog interfaces
- Integrated wireless communication
- Instruction cycle time
- Memory (size, type, expandable or not)
- Registers size (8/16/32 bits)
- Packaging
- etc.
Other important characteristics: hardware tools
- Development board
- Programmer, debugger
- Open source hardware
Other important characteristics: software tools
- Cross-compilation toolchain
- Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
- Open source software
Other important characteristics: support
- Professional support
- Active community (forums, examples...)
Some common microcontroller families
Arm
- UK company created in 1990
- There isn't any Arm microcontroller
- Arm provides Intellectual Property (IP) blocks, under a licensing agreement
- Among these blocks: RISC microcontrollers cores
- Low power, low cost: Cortex-M family
RISC: Reduced Instruction Set Computer
325 billions of Arm-based chips shipped.
Source:
Arm
Some Cortex-M licensees:
Cortex-M
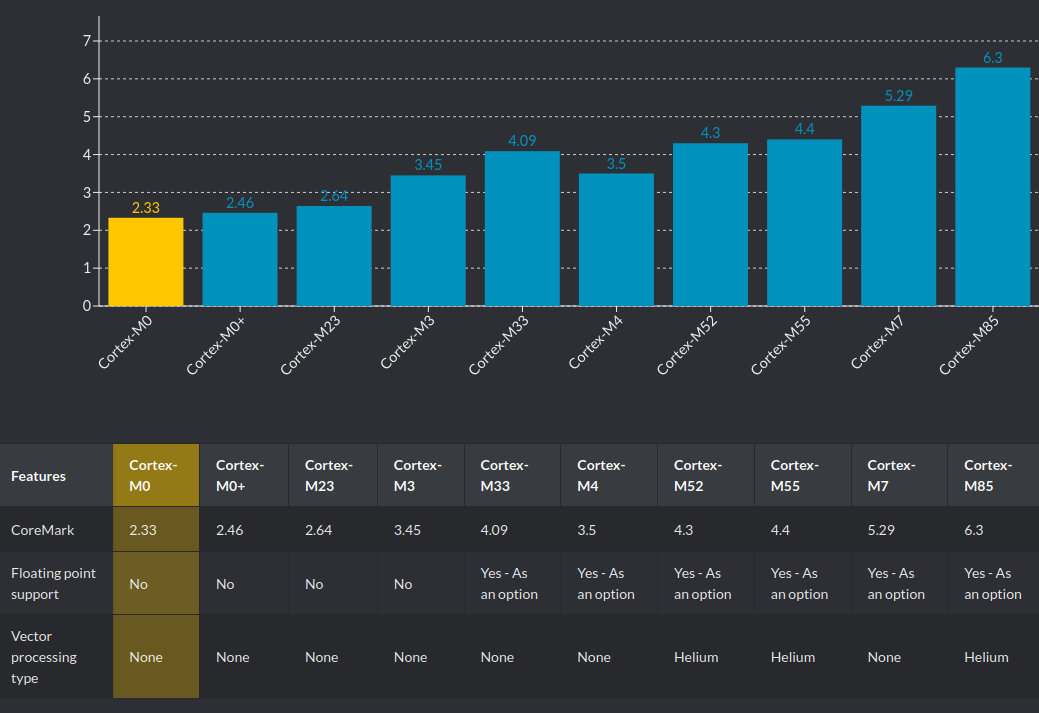
Source: Arm
Facilities for ML applications on Cortex-M
- Software library: CMSIS-NN - open-source library maximizing NN performance
- Hardware extension: FPU
- Hardware extension: DSP
- Hardware extension: Helium - vector extension
- Hardware extension: Ethos-U55 - NPU
CMSIS-NN: Common Microcontroller Software Interface Standard - Neural Network
FPU: Floating-Point Unit
DSP: Digital Signal Processing
NPU: Neural Processing Unit
FPU: Floating-Point Unit
DSP: Digital Signal Processing
NPU: Neural Processing Unit
Example: STMicroelectronics - STM32 family
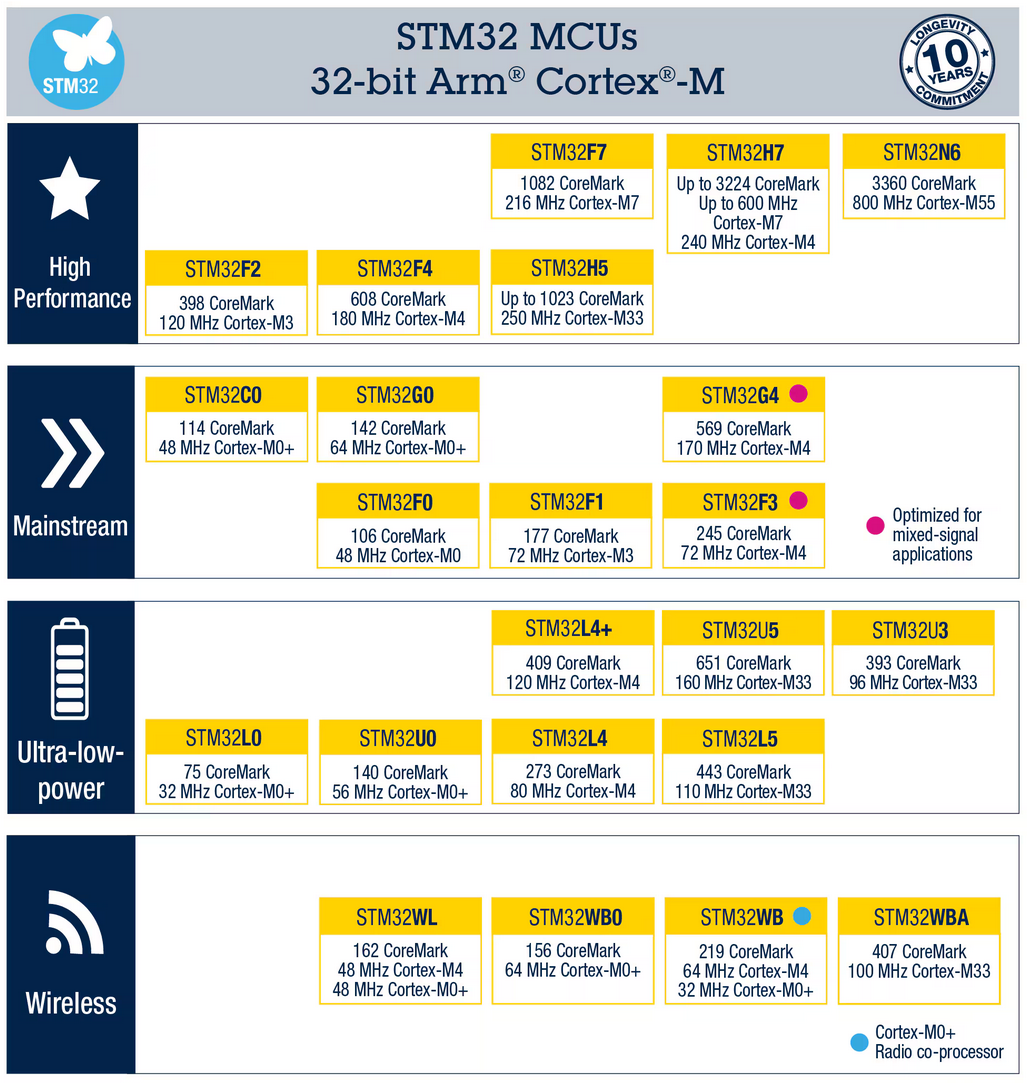
Source: STMicroelectronics
STM32L073RZ
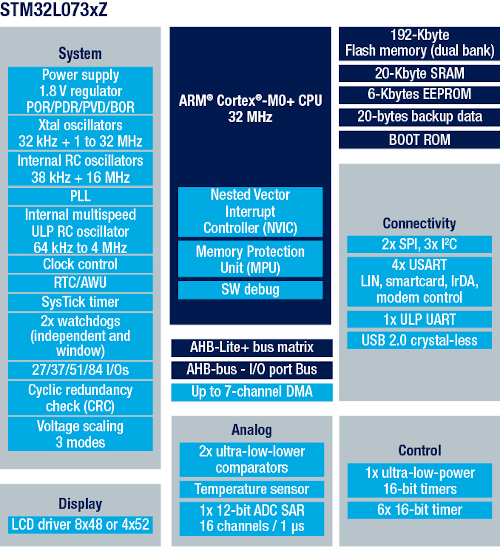
Source: STMicroelectronics
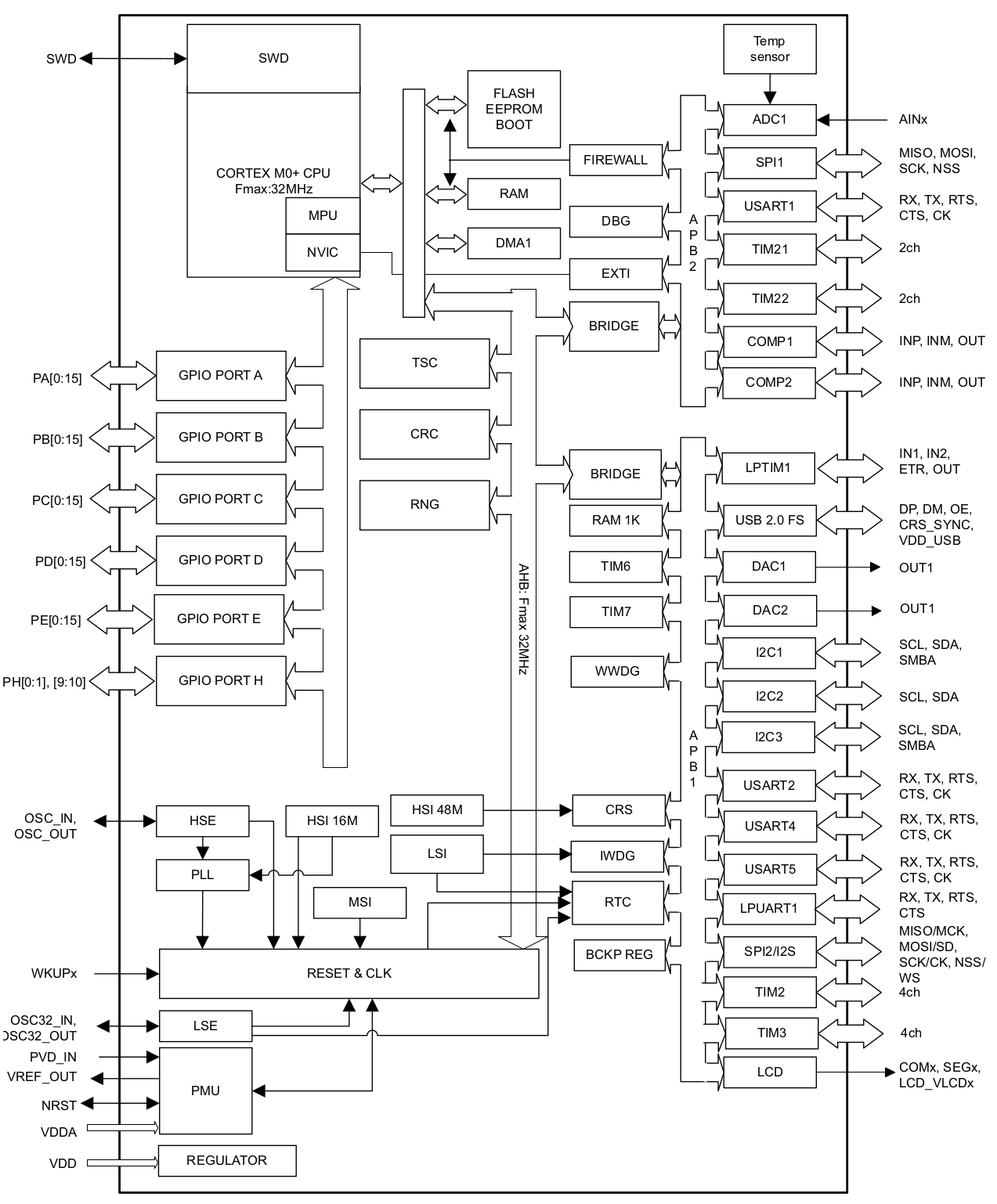
Source: STMicroelectronics
- Price: US$6.95 (unit) - US$2.66 (10,000)
Development board
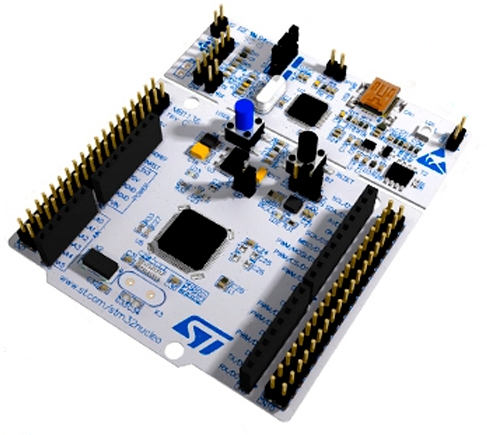
Price: US$16
Source: STMicroelectronics
STM32WL55

Source: STMicroelectronics
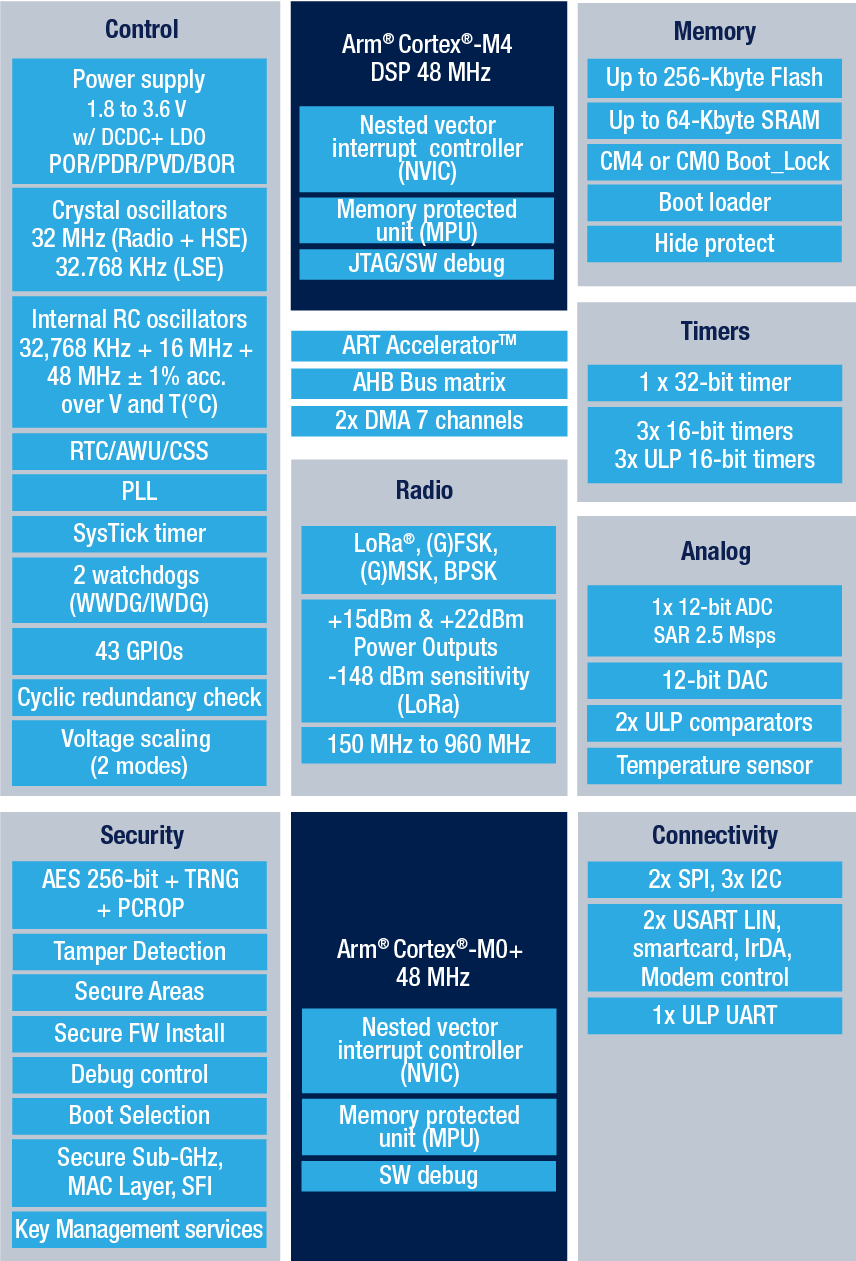
Source: STMicroelectronics
- Price: US$7.75 (unit) - US$4.54 (10,000)
Development board
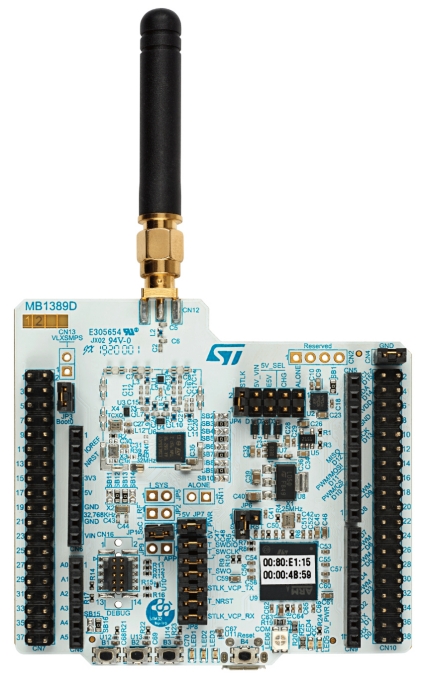

US$53
Source: STMicroelectronics
STM32N6 series
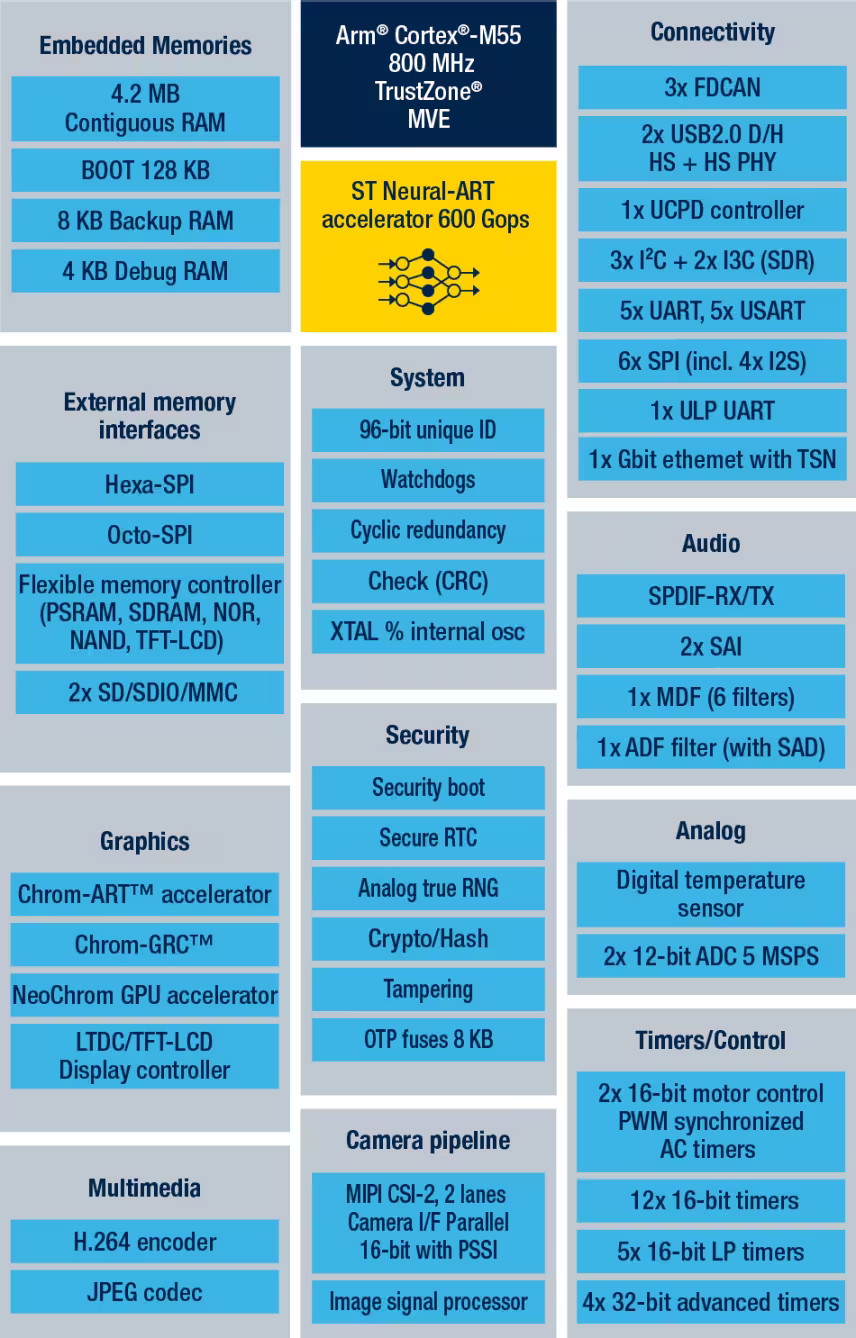
Source:
STMicroelectronics
Development board

US$78
Source:
STMicroelectronics
Example: Silicon Labs - EFR32 family
Source:
Silicon Labs Wireless SoCs
- Bluetooth: EFR32BG21, EFR32BG22, EFR32BG24, EFR32BG26, EFR32BG27
- Wi-Fi: SiWx915, SiWx917, RS9116, WF200
- Thread: EFR32MG12, EFR32MG13, EFR32MG21, EFR32MG24
- Etc.
EFR32MG24
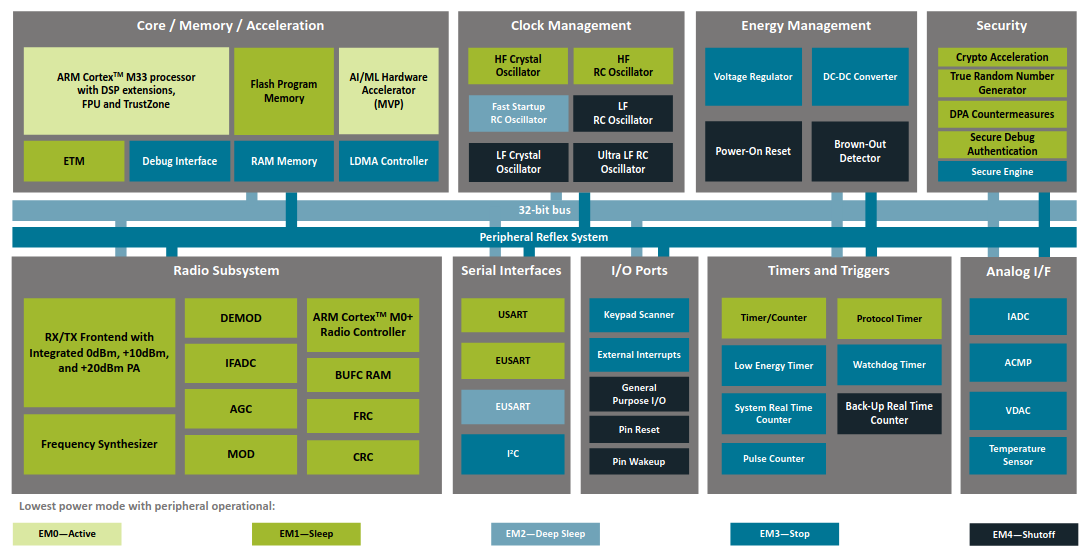
Source:
EFR32MG24 Datasheet
Matrix Vector Processor (MVP) - hardware accelerator for (complex) vector and matrix operations.
The MVP Math Library provides the associated API.
API: Application Programming Interface
- Price: around US$7 (unit)
Development board
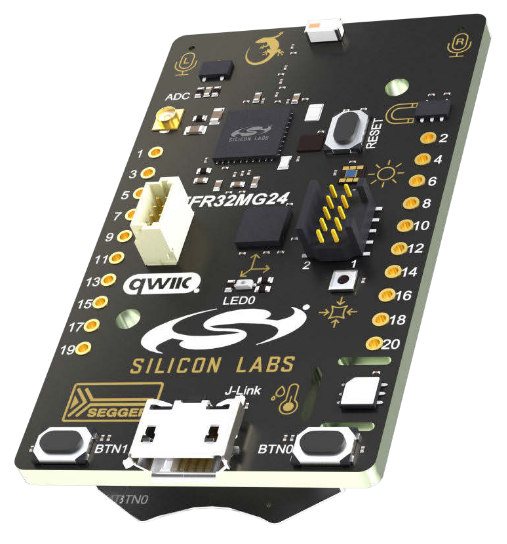

US$79
Source:
xG24 Dev Kit User's Guide
Espressif - ESP family

Espressif family
- ESP32-P Series - high-power RISC-V dual-core + low-power single-core
- ESP32-S Series - Xtensa LX7 dual-cor or single-core - Wi-Fi, BLE
- ESP32-C Series - RISC-V dual-core or single-core - Wi-Fi (2.4 GHz / 5 GHz), BLE, IEEE 802.15.4
- ESP32-H Series - RISC-V single-core
- ESP32 Series - Xtensa LX6 dual-core or single-core - Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, BLE
BLE: Bluetooth Low Energy
IEEE 802.15.4: physical layer and MAC layer for Zigbee, 6LowPAN, Thread, Matter, etc.
Source: Espressif
A note about RISC-V
RISC-V is an open, royalty-free instruction set architecture (ISA).
The RISC-V International Association drives the development of RISC-V.
ESP32-C6FH4
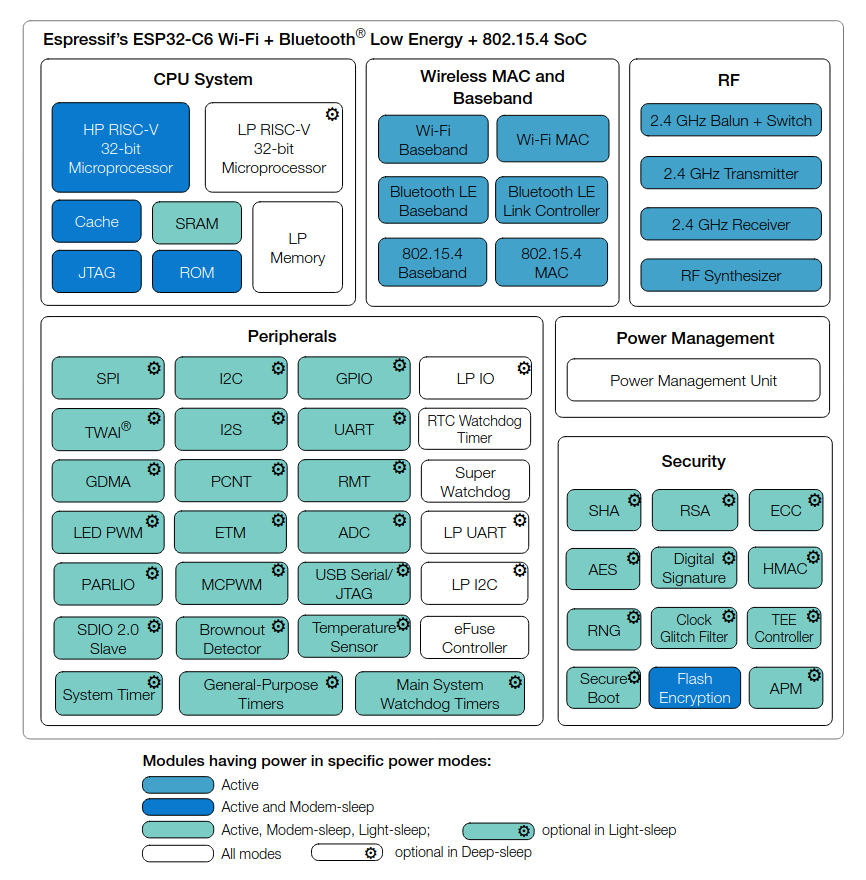
Source:
ESP32-C6 Datasheet
Some of the features
- High-power RISC-V processor - clock up to 160 MHz
- Low-power RISC-V processor - clock up to 20 MHz
- L1 cache: 32 KB
- ROM: 320 KB
- Hig-power SRAM: 512 KB
- Low-power SRAM: 16 KB
- Flash: 4 MB
- Price: US$2.05
Development board
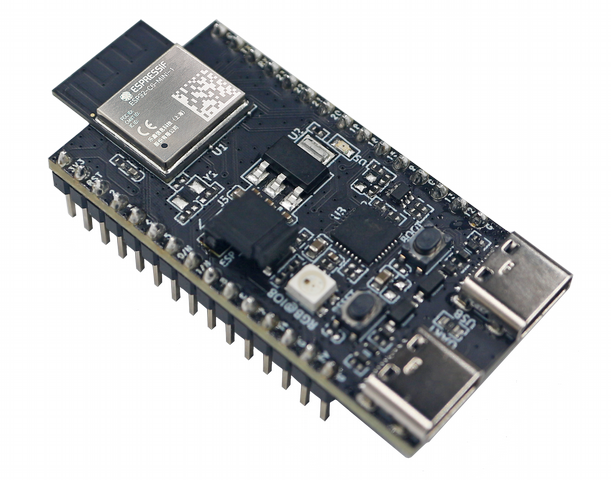
Source:
ESP32-C6-DevKitM-1
- Price: US$7.96
For ML
ESP32-S3: vector instructions - ESP-DSP and ESP-NN libraries
ESP32-P4: instruction extensions (vector, complex, etc.)