Software development - design pattern
Finite State Machine (FSM)
Finite State Machine
- Abstract machine having a finite number of states
- At a given time, is in one state
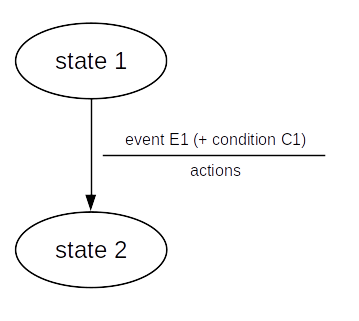
- Entering a new state (transition) is caused by an event
- A condition may guard a transition
- Processing is performed when transitioning
Also named Finite State Automaton (FSA)
A way to depict an FSM:
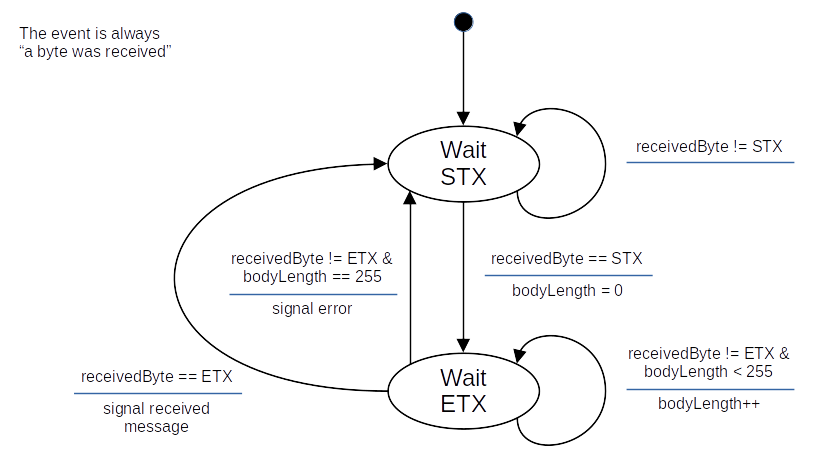
Example: a message receiver
A PC needs to send text messages to another PC. The two PCs are connected by a link with the following properties:
- Reliable (every sent byte is received, without error)
- In order
Every message is formatted as follows:
- Starts with the ASCII character STX (0x02)
- Ends with the ASCII character ETX (0x03)
- Message body contains alphanumeric characters (letters and numbers) only
- Message body contains a maximum of 255 characters
Possible FSM waiting for a full message:
A possible implementation:
current_state = WAIT_STX;
while (true) {
c = get_character();
switch (current_state) {
case WAIT_STX:
if (c == STX) {
body_length = 0
current_state = WAIT_ETX;
break;
}
// At this stage, other character, stay in this state.
break;
case WAIT_ETX:
if (c != ETX) {
if (body_length < 255) {
// TODO: store received byte.
body_length++;
// Stay in same state.
break;
}
// At this stage, body_length >= 255.
// TODO: signal error.
current_state = WAIT_STX;
break;
}
// At this stage, ETX.
current_state = WAIT_STX;
break;
default:
signal_error(UNKNOWN_STATE);
current_state = WAIT_STX;
}
}