Tasks
Task: a long-living execution block.
- The application is made of several tasks.
- These tasks may have to exchange data and to synchronize.
- Each task has its own execution context
- Each task can be assigned a priority
- Each task is assigned a "fair" proportion of processing time by the scheduler
A task may be in one of several states. Usually:
- Ready: the task is ready to run, but another one is using the processor
- Running: the task is being executed
- Blocked (or Waiting): the task is waiting for an event (timer timeout, reception of a byte on a serial link, etc.)
- Suspended: the task won't use the processor anymore
For FreeRTOS:
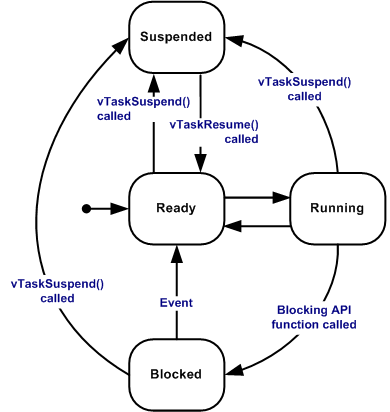
Source: FreeRTOS
Note: for our practice sessions, we will use FreeRTOS
For Zephyr OS:
Source: Zephyr Project
On a microcontroller with one core: only one task can be executed at a given time.
⇒ Difference between concurrency and parallelism:
- Concurrency: several tasks appear to be running at the same time
- Parallelism: several tasks are really running at the same time
The scheduler is the magic behind concurrency.
Scheduling method depends on the RTOS.
For FreeRTOS:
- Fixed priority - task priority is not changed (excepted for priority inheritance - see farther)
- Preemptive - if a higher priority task enters ready state (due to some event), and a lower priority task is being executed, the scheduler stops it and starts the higher priority one
- Round-robin time slicing - every task in the set of tasks with same priority is guaranteed to be executed after some time
When a task requests to wait for some event:
- The task enters the blocked (waiting) state
- The scheduler schedules the task with the highest priority, having waited for the longest time period
When a task with a given priority loops, for instance polling for an event without waiting for it:
- Tasks with lower priority will never be executed.
API example
task_handle_t task_create(...)status_t task_delete(task_handle_t th)status_t task_priority_set(task_handle_t th)status_t task_suspend(task_handle_t th)status_t task_resume(task_handle_t th)...
A good overview of task scheduling is provided by the FreeRTOS website.
Practice session 11
Creating and starting one task
- Purpose: make a LED blink using a task
- What to do: follow the instructions provided by the
embedded-systems-for-ML/practice-sessions/11-Start-task/README.mdfile